Dry Bulk Primer
There are four main, largely independent sectors within cargo shipping
Bulk Carriers
Iron ore, coal, grains, potash, fertilizers, cement, bauxite


Tankers
Crude oil and products, chemicals, vegetable oils


Container Ships
Dry container boxes, refrigerated, tanks


LNG Carriers
Liquefied Natural Gas


Our Focus: Dry-Bulk
Bulk carriers are categorized by their total cargo capacity, measured in Deadweight Tonnage (DWT)
- While flexible in terms of loading specific cargo, bulk carriers do show an affinity to specific commodities and trade routes depending on capacity
- There are four main types of vessels that operate in the dry-bulk segment: Capesize, Panamax, Supramax, Handysize


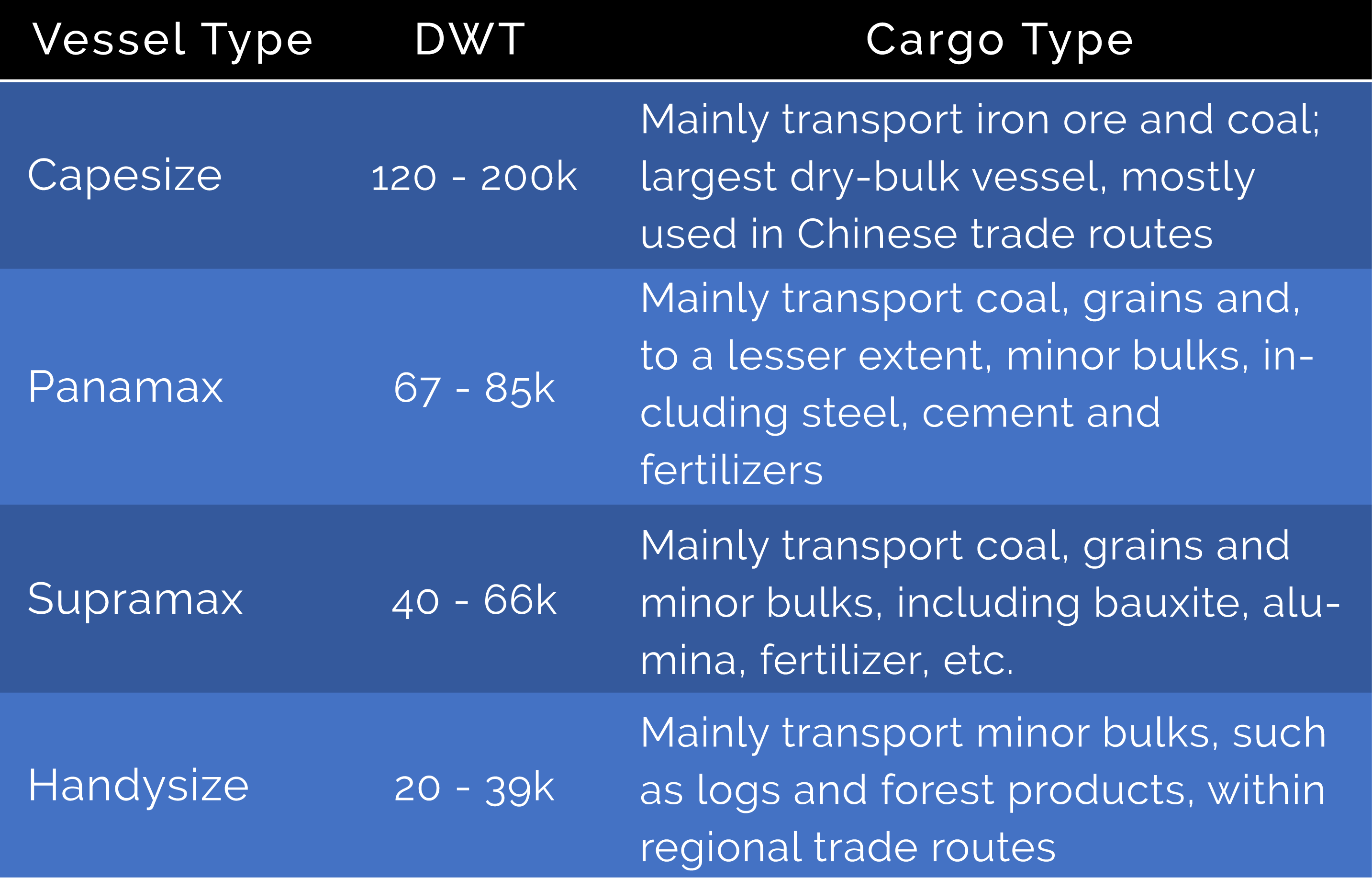
Vessel Comparison
Bulk carriers are usually identified by DWT capacity (size), country of construction, and delivery year
- Shipyard reputation, vessel particulars, dry-dock history, and numerous other factors affect vessel valuation
- Despite some variability, a bulk carrier still is a “commodity” that carries another commodity and has a verifiable market value


